43 zero coupon bonds risk
Understanding Bonds: The Types & Risks of Bond Investments Zero-coupon bonds and Treasury bills are exceptions: The interest income is deducted from their purchase price and the investor then receives the full face value of the bond at maturity. All bonds carry some degree of "credit risk," or the risk that the bond issuer may default on one or more payments before the bond reaches maturity. Zero-Coupon Bond: Formula and Calculator - Wall Street Prep Zero-Coupon Bond Risks Interest Rate Sensitivity One drawback to zero-coupon bonds is their pricing sensitivity based on the prevailing market interest rate conditions. Bond prices and interest rates have an "inverse" relationship with one another: Declining Interest Rates Higher Bond Prices Rising Interest Rates Lower Bond Prices
Zero-Coupon Bond - Definition, How It Works, Formula 28/01/2022 · Understanding Zero-Coupon Bonds. As a zero-coupon bond does not pay periodic coupons, the bond trades at a discount to its face value. To understand why, consider the time value of money.. The time value of money is a concept that illustrates that money is worth more now than an identical sum in the future – an investor would prefer to receive $100 today …

Zero coupon bonds risk
What are Zero-Coupon Bonds? (Definition, Formula, Example, Advantages ... From an investor's perspective, zero coupon bonds have the following advantages: They are safe investment instruments and have a lower element of risk involved. Long Dated zero coupon bonds are the most responsive to interest rate fluctuations. Therefore, it might be profitable for the bondholder in the case of a long duration (a higher 'N'). Zero Coupon Bond | Investor.gov Zero coupon bonds are bonds that do not pay interest during the life of the bonds. Instead, investors buy zero coupon bonds at a deep discount from their face value, which is the amount the investor will receive when the bond "matures" or comes due. The maturity dates on zero coupon bonds are usually long-term—many don’t mature for ten ... What are zero-coupon bonds? - moneycontrol.com 07/09/2022 · Zero coupon bonds are issued at a discount to the face value of the bond. They do not pay interest during the tenure of the security. The investor of the zero coupon bond receives the face value ...
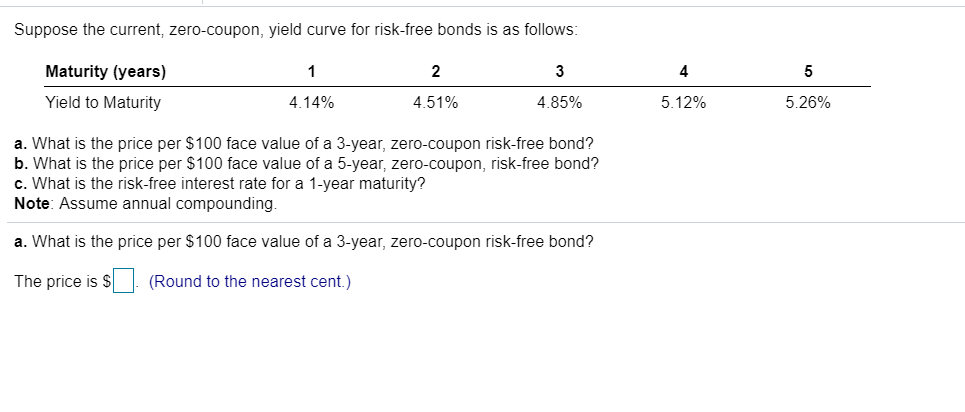
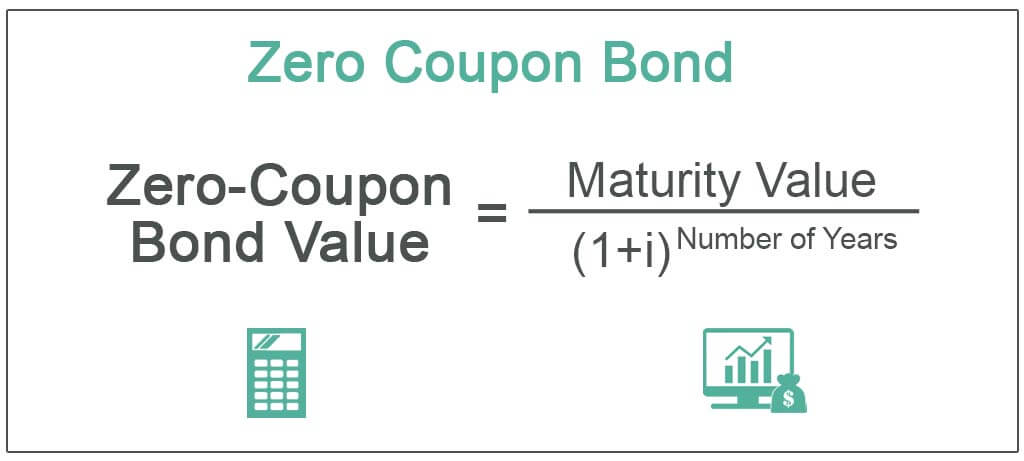
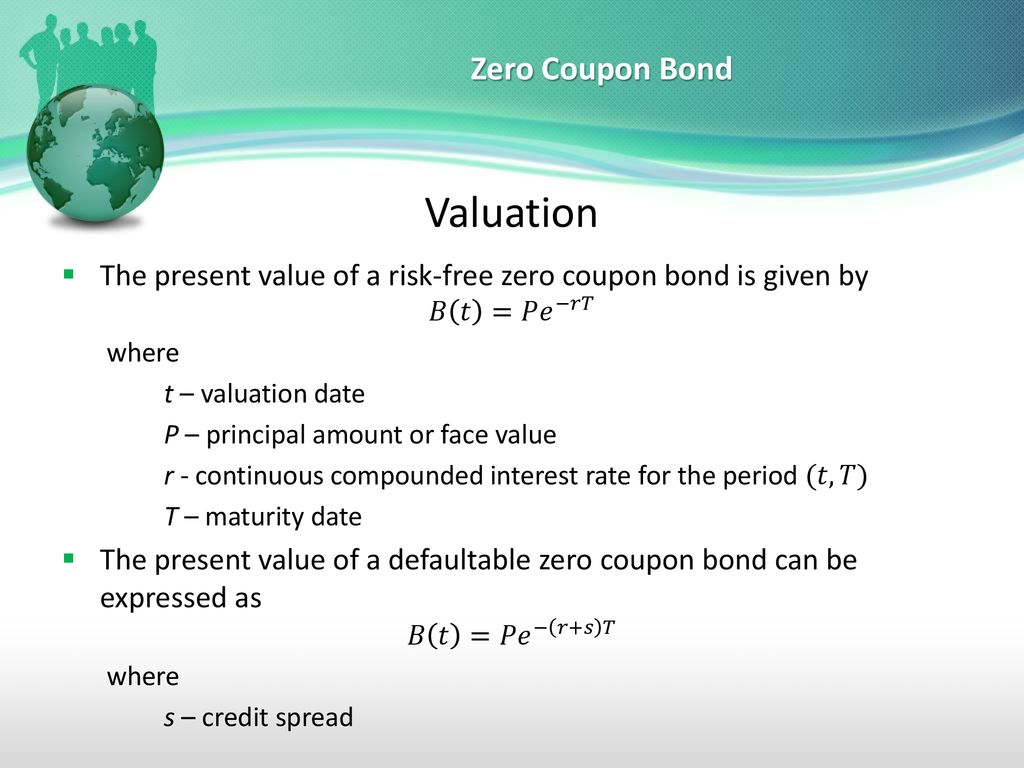
Zero coupon bonds risk. Zero coupon bonds are back in flavour. Will the party continue? 06/09/2022 · “Zero coupon bonds are highly beneficial when the interest rates are high and there is no re-investment risk during the life period of the bond for the investors,” said Srinivasan of Rockfort ... Zero-Coupon Bond Value | Formula, Example, Analysis, Calculator The value of a zero-coupon bond is determined by its face value, maturity date, and the prevailing interest rate. The formula to calculate the value of a zero-coupon bond is. Price = M / (1+r)n. where: M = maturity value or face value of the bond. r = rate of interest required. n = number of years to maturity. 3. How to Buy Zero Coupon Bonds | Finance - Zacks The bonds are sold at a deep discount, and the principal plus accrued interest is paid at the bond's maturity date. The less you pay for a zero coupon bond, the higher the yield. A bond with a ... All the 21 Types of Bonds | General Features and Valuation | eFM 13/06/2022 · Zero-Coupon Bonds. A zero-coupon bond is a type of bond with no coupon payments. It is not that there is no yield; the zero-coupon bonds are issued at a price lower than the face value (say 950$) and then pay the face value on maturity ($1000). ... Since the government agency issues the bonds, they are almost risk-free, or at least both are ...
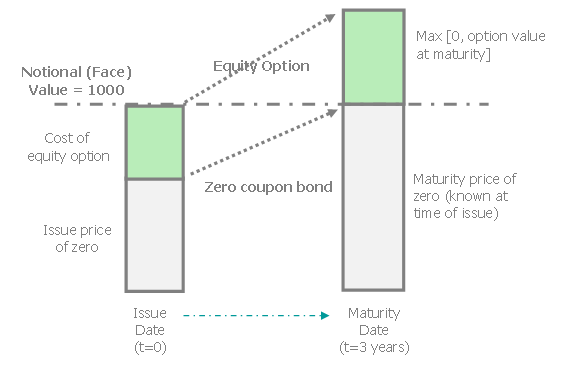
Zero-Coupon Bond - Definition, How It Works, Formula A zero-coupon bond is a bond that pays no interest. The bond trades at a discount to its face value. Reinvestment risk is not relevant for zero-coupon bonds, but interest rate risk is relevant for the bonds. Understanding Zero-Coupon Bonds As a zero-coupon bond does not pay periodic coupons, the bond trades at a discount to its face value. Advantages and Risks of Zero Coupon Treasury Bonds - Investopedia Unique Risks of Zero-Coupon U.S. Treasury Bonds Because of their sensitivity to interest rates, zero-coupon Treasury bonds have incredibly high interest rate risk. Treasury zeros fall significantly... Use of Government Bonds in calculating risk-free rates - Refinitiv This article explains what Net Present Values, Face Values, Maturities, Coupons, Yield to Maturity, compound frequency, Coupon rates and risk-free rates are, how to compute them, and how they are used to calculate excess returns using only Zero-Coupon Bonds; other types of bonds are discussed for completeness, but they will only be investigated as such in further articles to come. It is aimed ... Zero Coupon Bond | Investor.gov Because zero coupon bonds pay no interest until maturity, their prices fluctuate more than other types of bonds in the secondary market. In addition, although no payments are made on zero coupon bonds until they mature, investors may still have to pay federal, state, and local income tax on the imputed or "phantom" interest that accrues each year.
Zero Coupon Bonds- Taxability Under Income Tax Act, 1961 - TaxWink Zero Coupon Bonds carries lesser risk with fixed income option. The return on these bonds is comparably higher as compared to other fixed income options. Further, the most important advantage of the zero coupon bonds is that no tax is payable on interest element if you invest in notified zero coupon bonds. Zero-Coupon Bonds: Pros and Cons - Management Study Guide Higher Yields: Firstly, zero-coupon bonds are perceived as higher-risk bonds. This is because investors pay money upfront and then do not have much control over it. Also, since the money is locked in over longer periods of time, the perceived risk is more. Zero Coupon Muni Bonds - What You Need to Know - MunicipalBonds.com The problem with traditional bonds is that investors must reinvest the semiannual interest payments at potentially lower interest rates. Since investors can lock in a specific rate of return with zero coupon bonds, they are spared from worrying about reinvesting the capital at a later date and thereby avoid any reinvestment risks. What Are Zero Coupon Bonds And Their Risks- Tavaga | Tavagapedia Risks associated with Zero-Coupon Bonds. As there is no coupon rate, ZCBs are safer as compared to other fixed-income instruments, which are sensitive to changes in interest rates. But ZCBs do possess risk subjected to changes in interest rates if sold before maturity. The value of ZCB and interest rate are inversely related, so an increase in ...
How to Invest in Zero-Coupon Bonds - US News & World Report Zeros are purchased through a broker with access to the bond markets, or with an actively managed mutual fund or and index-style product like an exchange-traded fund. PIMCO 25+ Year Zero Coupon US ...
Zero-Coupon Bond Definition - Investopedia Zero-coupon bonds are like other bonds, in that they do carry various types of risk, because they are subject to interest rate risk if investors sell them before maturity. How Does a Zero-Coupon...
Zero Coupon Bond - (Definition, Formula, Examples, Calculations) Zero-Coupon Bond (Also known as Pure Discount Bond or Accrual Bond) refers to those bonds which are issued at a discount to its par value and makes no periodic interest payment, unlike a normal coupon-bearing bond. In other words, its annual implied interest payment is included in its face value which is paid at the maturity of such bond.
Should I Invest in Zero Coupon Bonds? | The Motley Fool Specifically, if rates rise, they make the value of your zero coupon bond go down, potentially forcing you to sell at a depressed price if your timing is bad. Another problem with zero coupon bonds...
Zero-coupon bond - Wikipedia A zero coupon bond (also discount bond or deep discount bond) is a bond in which the face value is repaid at the time of maturity. [1] Unlike regular bonds, it does not make periodic interest payments or have so-called coupons, hence the term zero-coupon bond. When the bond reaches maturity, its investor receives its par (or face) value.
Advantages and Risks of Zero Coupon Treasury Bonds - Investopedia 31/01/2022 · Zero-coupon U.S. Treasury bonds have a poor risk-return profile when held alone. Long-dated zero-coupon Treasury bonds are more volatile than the stock market, but they offer the lower long-run ...
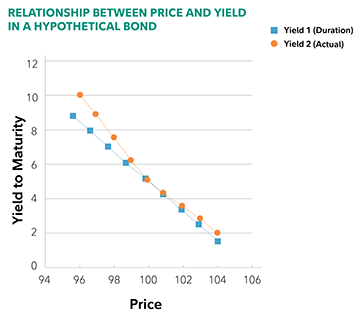
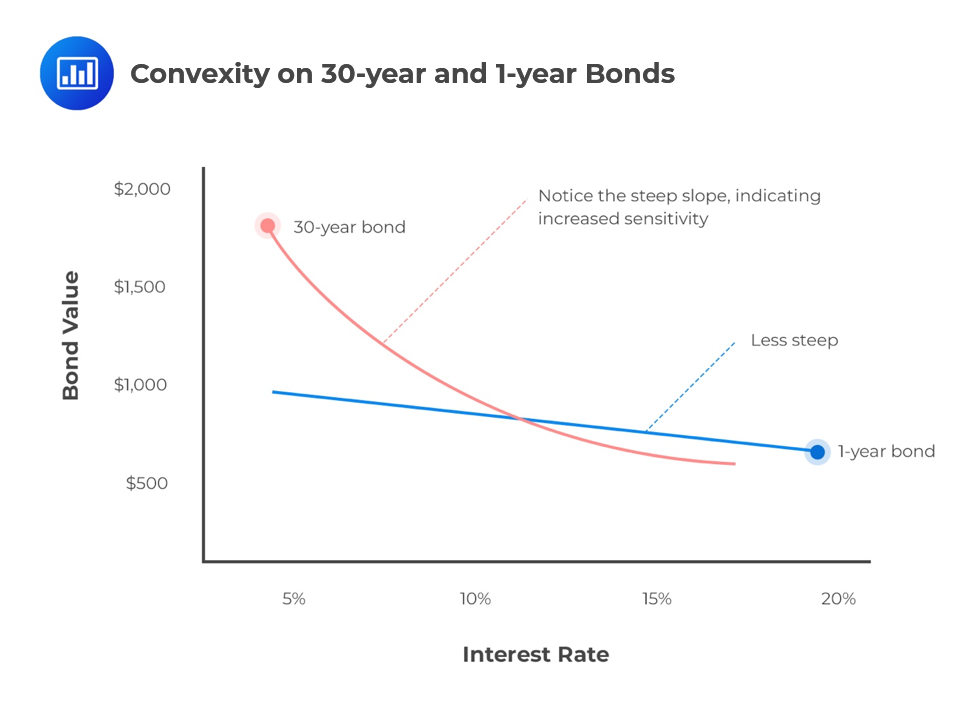
Why do zero coupon bonds have higher interest rate risk than bonds that ... Zero coupon bonds are more sensitive to changes in interest rates than bonds paying a coupon because the duration of a zero coupon bond is generally going to be higher than it would be for a bond of the same investment with the same term to maturity. Many people confuse bond duration with term to maturity, but they are not the same thing at all.
Do zero-coupon bonds have interest rate risk? - Quora Zeros always have exposure to the first type, and MIGHT have exposure to the second type. When people use the term "interest rate risk", they usually refer to the first type of risk (i.w. "price risk") - when interest rates change, it affects prices, and in the opposite direction to the change in rates.
Bonds Center - Bonds quotes, news, screeners and educational Bonds Center - Learn the basics of bond investing, get current quotes, news, commentary and more.
What Is a Zero-Coupon Bond? - The Motley Fool With zero-coupon bonds, interest rate risk is at its highest since zeros display unusual sensitivity to changes in interest rates -- although the underlying inverse relationship to interest rates...
Zero Coupon Bond: Meaning, Features & Advantages - BondsIndia Features of Zero-Coupon Bond. The difference between the purchase price of a zero-coupon bond and the par value, indicates the investor's return. Zero Coupon Bonds have no reinvestment risk however they carry interest rate risk. The accumulated interest is paid at the time of maturity. Includes a maturity period of 10 to 15 years.
What Is a Zero-Coupon Bond? Definition, Advantages, Risks As a result, zero-coupon bond prices are more volatile — subject to greater swings when interest rates change. You have to pay taxes on income you don't get Even though you're not actually getting...
Zero-Coupon Bonds : What is Zero Coupon Bond? - Groww No reinvestment risk: Other coupon bonds don't allow investors to a bond's cash flow at the same rate as the investment's required rate of returns. But the Zero Coupon bonds remove the reinvestment risk. Zero Coupon bonds do not allow any periodic coupon payments and thus a fixed interest on Zero Coupon bonds is assured.
Invest in G-SEC STRIPS India - Bondsindia.com Stripping is the process of separating a standard coupon-bearing bond into its individual coupon and principal components. For example, a 10 year coupon bearing bond can be stripped into 20 coupon and one principal instruments, all of which thenceforth would …
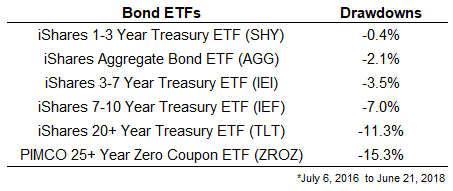
ZROZ ETF Report: Ratings, Analysis, Quotes, Holdings | ETF.com Since STRIPs are zero coupon bonds, they are particularly sensitive to interest-rate risk. As a result, the fund's effective duration is much higher, which in turn produces volatile results ...
Zero-Coupon Bond Definition - Investopedia 31/05/2022 · Zero-Coupon Bond: A zero-coupon bond is a debt security that doesn't pay interest (a coupon) but is traded at a deep discount, rendering profit at maturity when the bond is redeemed for its full ...
The Pros and Cons of Zero-Coupon Bonds - m.finweb.com Another problem with zero coupon bonds is that they have a higher default risk than traditional bonds. The reason behind this is that companies do not have to make regular interest payments to the investors. They just keep all of the money and do with it as they please.
Mapping Zero-coupon Bonds to Risk Factors - Finance Train The first coupon is sensitive to the 6-month interest rate, the next coupon is sensitive to the one-year interest rate, and the last (10th) payment will be sensitive to the 5-year zero-coupon interest rate. For the purpose of mapping each cash flow, the risk manager will need to identify a set of zero-coupon bonds at different maturities.
The One-Minute Guide to Zero Coupon Bonds | FINRA.org Like virtually all bonds, zero-coupon bonds are subject to interest-rate risk if you sell before maturity. If interest rates rise, the value of your zero-coupon bond on the secondary market will likely fall. Long-term zeros can be particularly sensitive to changes in interest rates, exposing them to what is known as duration risk.
What are zero-coupon bonds? - moneycontrol.com 07/09/2022 · Zero coupon bonds are issued at a discount to the face value of the bond. They do not pay interest during the tenure of the security. The investor of the zero coupon bond receives the face value ...
Zero Coupon Bond | Investor.gov Zero coupon bonds are bonds that do not pay interest during the life of the bonds. Instead, investors buy zero coupon bonds at a deep discount from their face value, which is the amount the investor will receive when the bond "matures" or comes due. The maturity dates on zero coupon bonds are usually long-term—many don’t mature for ten ...
What are Zero-Coupon Bonds? (Definition, Formula, Example, Advantages ... From an investor's perspective, zero coupon bonds have the following advantages: They are safe investment instruments and have a lower element of risk involved. Long Dated zero coupon bonds are the most responsive to interest rate fluctuations. Therefore, it might be profitable for the bondholder in the case of a long duration (a higher 'N').









/DurationandConvexitytoMeasureBondRisk2-0429456c85984ad3b220cd23a760cda5.png)











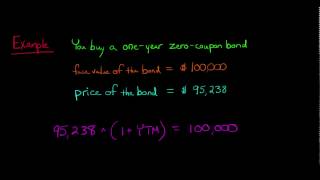








Post a Comment for "43 zero coupon bonds risk"